Making the UDL Case to Campus & School Leaders
This resource provides use-them-tomorrow strategies to get buy-in, advocacy, and support for UDL adoption from your president, provost, principal, school board, and other institutional leaders.
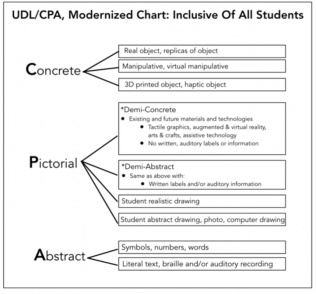
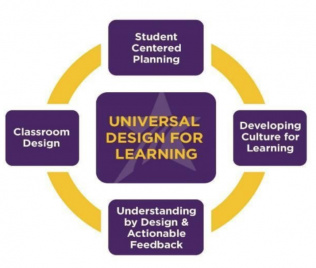
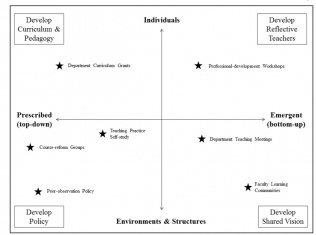
Only about ten percent of K-12, college, and university courses utilize any form of inclusive design (Lombardi, Murray, & Gerdes, 2011, p. 255). Campus leaders often see Universal Design for Learning (UDL) as a) benefitting only a small segment of learners; b) requiring a significant outlay of time, people, and work; and c) having a limited impact on learner outcomes. This white paper from the author of Reach Everyone, Teach Everyone: UDL in Higher Education(2018) provides use-them-tomorrow strategies to get buy-in, advocacy, and support for UDL adoption from your president, provost, principal, school board, and other institutional leaders.
Share this resource:
Posted date:
May 17, 2019
Access the full resource here if it does not render.